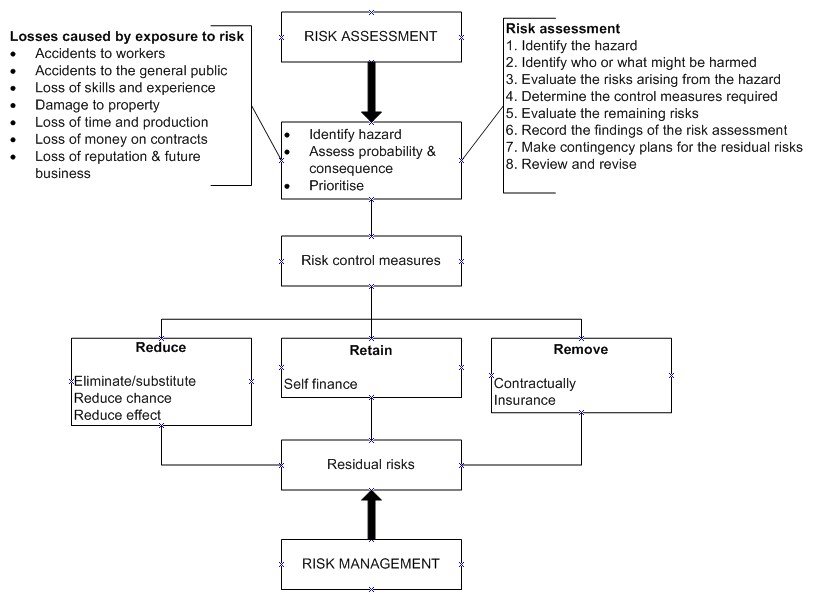
A common failure in managing risk is the lack of transparency. This was highlighted by the scandal over coronavirus fatalities. Additional problems include a lack data and siloed information. The process was not built with risk in view. Risk managers settle for easy access data and fail to recognize risks that could have serious consequences. This is a common problem, which is hard to fix, but must be avoided.
Negative risks
Managers have five options for managing negative risks and threats. These strategies depend on the kind of risk and the exposure level. They are also dependent on the likelihood of an occurrence and the effect it will have upon the project's objectives. These strategies, which are the most effective, are used when risk is considered critical. When the risk is less critical, the transfer and accept strategy can be used.
People, technology, resources, and processes are affected by both positive and negative risk. Positive risks can have positive results if they are managed correctly. If managed correctly, positive risks could lead to project completion sooner than expected and a greater return on investment. There are always negative risks. However, you can avoid them by using the best risk management practices. These risks are not without their challenges. They can have a negative impact on the project's timeline, budget, or schedule.

Communication
Communication is key to risk management. Communication must be honest and open, no matter whether it is via a formal document. Communication professionals can avoid misunderstanding the risk. However, it is possible to minimize this risk by keeping it honest and open. Hurricane Harvey is one example of how to communicate risks. In 2017, Hurricane Harvey was a devastating hurricane that threatened Houston. Public officials used local, national and social media communication to warn residents to evacuate. Professionals must direct people to reliable sources for information.
Poor communication is one of the greatest risks when managing a project. If there is poor communication, it can make or break a project. Communication is key to employee engagement and reducing miscommunications. An assessment of project management risks should include communication enhancement activities. Once it is done, project managers may take steps to mitigate the risk. This includes using a communication risk assessment tool and including stakeholders in the process.
Consultation
A project's risk management requires that all stakeholders be included. These stakeholders could include both internal and outside partners, as well stakeholders who are not directly involved with the project. Engaging key stakeholders is essential in order to ensure all parties are aware of the risks and expectations. To ensure the appropriate level of consultation, project teams should involve all stakeholders during the risk assessment and management process. Here are some tips for ensuring that the consultation process involves all key stakeholders.
Risk management consultants will assist in prioritizing risks. This is critical because higher-risk risks will need immediate attention while lower risk ones will require a more gradual remediation strategy. Consulting is a great way for organizations to identify risks and design a risk management program that meets their specific needs. Consultants will also assist with the development of an action plan that will help the organization mitigate risks and improve its overall risk management process.
Top-down
There are clear advantages and disadvantages to top down risk management. To start up it requires considerable time, effort, as well as expertise. It can be very individualized, so what one manager may have learned in one industry may not work for another. It has tremendous potential to be used as a risk management tool. It is slowly becoming more widely accepted, even though it isn't widely used. These are just a few reasons.
The initial stages of a project are the most beneficial for top-down risk management. The benefits of risk management at this stage are the greatest. Previous projects' experience can easily be applied. Top-down management accountability can be enhanced by top-down models and methods from previous projects that are evidence-based. Top-down risk management techniques are a great way to reduce project risk if they are used correctly. Additionally, they can help managers or teams meet their financial obligations toward stakeholders.
FAQ
How can we create a successful company culture?
A positive company culture creates a sense of belonging and respect in its people.
It is founded on three basic principles:
-
Everyone has something valuable to contribute
-
People are treated fairly
-
It is possible to have mutual respect between groups and individuals
These values reflect in how people behave. They will treat others with consideration and courtesy.
They will respect other people's opinions.
They can also be a source of inspiration for others.
In addition, the company culture encourages open communication and collaboration.
People feel free to express their views openly without fear of reprisal.
They understand that mistakes can be forgiven as long as they're dealt with honestly.
The company culture encourages honesty and integrity.
Everyone is aware that truth must be told.
Everyone understands that there are rules and regulations which apply to them.
Nobody expects to be treated differently or given favors.
What are management theories?
Management Concepts are the principles and practices managers use to manage people and resources. These include topics such as human resource policies and job descriptions, performance assessments, training programs and employee motivation.
What is the best way to motivate your employees as a manager?
Motivation refers to the desire or need to succeed.
Enjoyable activities can motivate you.
You can also be motivated by the idea of making a difference to the success and growth of your organization.
For example: If you want to be a doctor, you might find it more motivating seeing patients than reading medical books all day.
A different type of motivation comes directly from the inside.
You may feel strongly that you are responsible to help others.
Perhaps you enjoy working hard.
If you don’t feel motivated, find out why.
Next, think of ways you can improve your motivation.
What are the 3 basic management styles?
The three major management styles are authoritarian (left-faire), participative and laissez -faire. Each style is unique and has its strengths as well as weaknesses. Which style do YOU prefer? Why?
Authority - The leader is the one who sets the direction and expects everyone in the organization to follow it. This style is most effective when an organization is large, stable, and well-run.
Laissez-faire: The leader lets each person decide for themselves. This approach works best in small, dynamic organizations.
Participative - Leaders listen to all ideas and suggestions. This is a great style for smaller organizations that value everyone.
Why does it sometimes seem so hard to make good business decisions
Businesses are complex systems, and they have many moving parts. People who manage them have to balance multiple priorities while dealing with complexity and uncertainty.
To make good decisions, you must understand how these factors affect the entire system.
This requires you to think about the purpose and function of each component. Next, consider how each piece interacts with the others.
Also, you should ask yourself if there have been any assumptions in your past behavior. If they don't, you may want to reconsider them.
For help, ask someone else if you're still stumped after all the above. You may be able to see things from a different perspective than you are and gain insight that can help you find a solution.
What kind people use Six Sigma?
Six Sigma will most likely be familiar to people who have worked in statistics and operations research. But anyone can benefit from it.
It is a commitment-intensive task that requires strong leadership skills.
Statistics
- The average salary for financial advisors in 2021 is around $60,000 per year, with the top 10% of the profession making more than $111,000 per year. (wgu.edu)
- The profession is expected to grow 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average. (wgu.edu)
- Our program is 100% engineered for your success. (online.uc.edu)
- This field is expected to grow about 7% by 2028, a bit faster than the national average for job growth. (wgu.edu)
- The BLS says that financial services jobs like banking are expected to grow 4% by 2030, about as fast as the national average. (wgu.edu)
External Links
How To
What is Lean Manufacturing?
Lean Manufacturing processes are used to reduce waste and improve efficiency through structured methods. They were developed by Toyota Motor Corporation in Japan during the 1980s. The primary goal was to make products with lower costs and maintain high quality. Lean manufacturing is about eliminating redundant steps and activities from the manufacturing process. It consists of five basic elements: pull systems, continuous improvement, just-in-time, kaizen (continuous change), and 5S. Pull systems allow customers to get exactly what they want without having to do extra work. Continuous improvement is constantly improving upon existing processes. Just-in–time refers when components or materials are delivered immediately to their intended destination. Kaizen stands for continuous improvement. Kaizen can be described as a process of making small improvements continuously. Finally, 5S stands for sort, set in order, shine, standardize, and sustain. These five elements work together to produce the best results.
Lean Production System
The lean production system is based on six key concepts:
-
Flow - focuses on moving information and materials as close to customers as possible.
-
Value stream mapping: This is a way to break down each stage into separate tasks and create a flowchart for the entire process.
-
Five S's: Sort, Shine Standardize, Sustain, Set In Order, Shine and Shine
-
Kanban: Use visual signals such stickers, colored tape, or any other visual cues, to keep track your inventory.
-
Theory of constraints - identify bottlenecks during the process and eliminate them with lean tools like Kanban boards.
-
Just-in time - Get components and materials delivered right at the point of usage;
-
Continuous improvement - Make incremental improvements rather than overhauling the entire process.